Creating a batch change
Batch changes are created by writing a batch spec and executing that batch spec with the Sourcegraph CLI src.
Batch changes can also be used on multiple projects within a monorepo by using the workspaces key in your batch spec.
There are two paths to creating a batch change:
- On your local machine, with the Sourcegraph CLI
- Remotely, with server-side execution
Many concepts are shared between the two paths. However, this guide will walk you through creating a batch change the first way, on your local machine.
Requirements
- Sourcegraph instance with repositories in it. See the "Quickstart" guide on how to setup a Sourcegraph instance.
- Installed and configured Sourcegraph CLI (see "Install the Sourcegraph CLI" in the Batch Changes quickstart for detailed instructions).
- Configured credentials for the code host(s) that you'll be creating changesets on. See "Configuring user credentials" for a guide on how to add and manage credentials.
Writing a batch spec
In order to create a batch change, you need a batch spec that describes the batch change. Here is an example batch spec that describes a batch change to add "Hello World" to all README files:
name: hello-world
description: Add Hello World to READMEs
# Find all repositories that contain a README file.
on:
- repositoriesMatchingQuery: file:README
# In each repository, run this command. Each repository's resulting diff is captured.
steps:
- run: IFS=$'\n'; echo Hello World | tee -a $(find -name README)
container: alpine:3
# Describe the changeset (e.g., GitHub pull request) you want for each repository.
changesetTemplate:
title: Hello World
body: My first batch change!
branch: hello-world # Push the commit to this branch.
commit:
message: Append Hello World to all README files
published: false # Do not publish any changes to the code hosts yetThe commits created from your spec will use the git config values for user.name and user.email from your local environment, or "batch-changes@sourcegraph.com" if no user is set. Alternatively, you can also specify an author in this spec.
See the "batch spec YAML reference" and the tutorials for more details on how to write batch specs.
Creating a batch change after previewing
After writing a batch spec you use the Sourcegraph CLI (src) to execute the batch spec and upload it to Sourcegraph, where you can preview the changes and apply the batch spec to create a batch change:
-
Run the following command in your terminal:
src batch preview -f YOUR_BATCH_SPEC.batch.yamlDon't worry! Before any branches are pushed or changesets (e.g., GitHub pull requests) are created, you will see a preview of all changes and can confirm each one before proceeding. NOTE: Batch Changes's default behavior is to stop if computing changes in a repository errors. You can choose to ignore errors instead by adding the
skip-errorsflag :src batch preview -f spec.batch.yml -skip-errors -
Wait for it to run and compute the changes for each repository (using the repositories and commands in the batch spec).
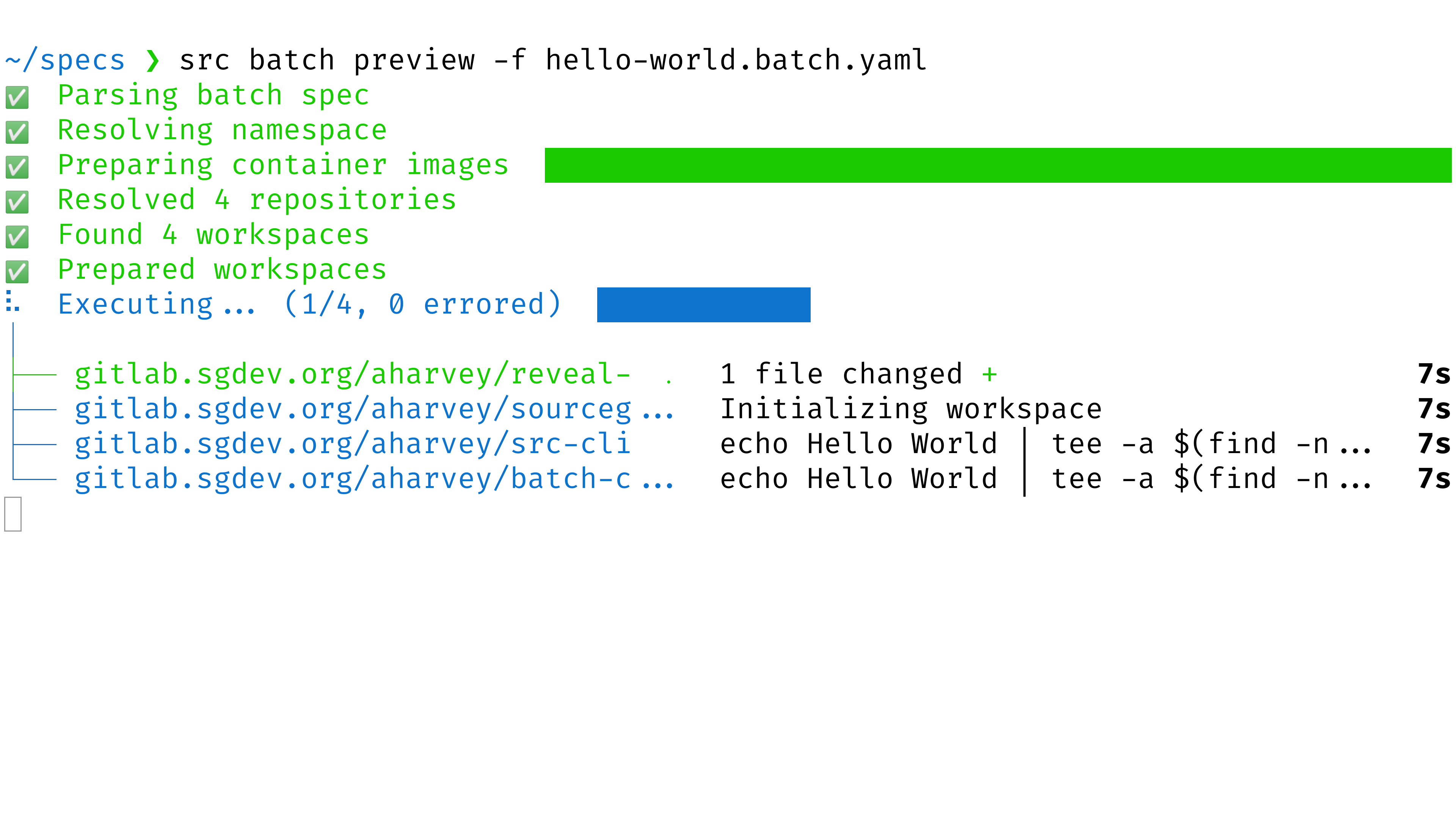
-
Open the preview URL that the command printed out.
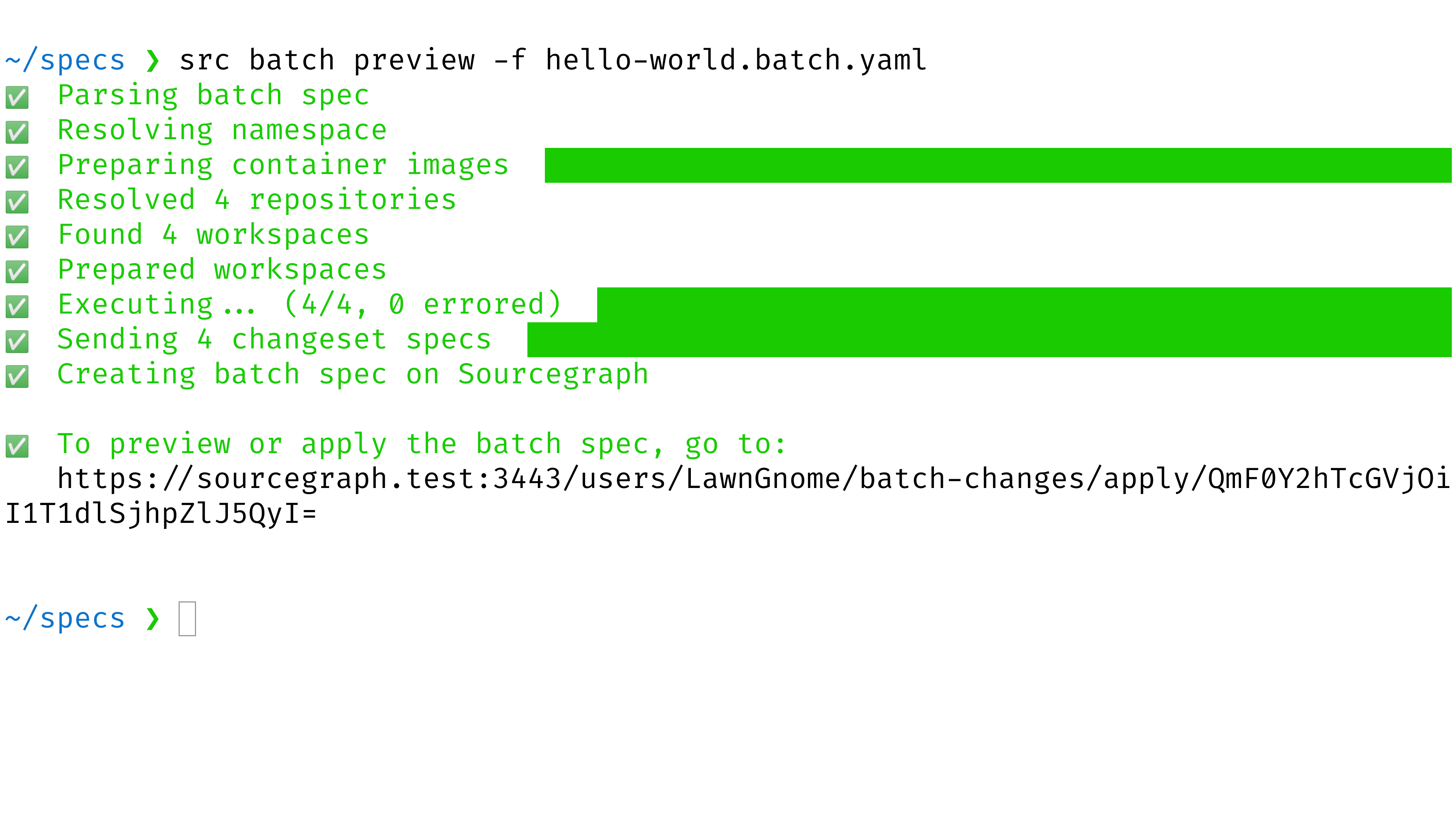
-
Examine the preview. This is the result of executing the batch spec. Confirm that the changes are what you intended. If not, edit the batch spec and then rerun the command above.
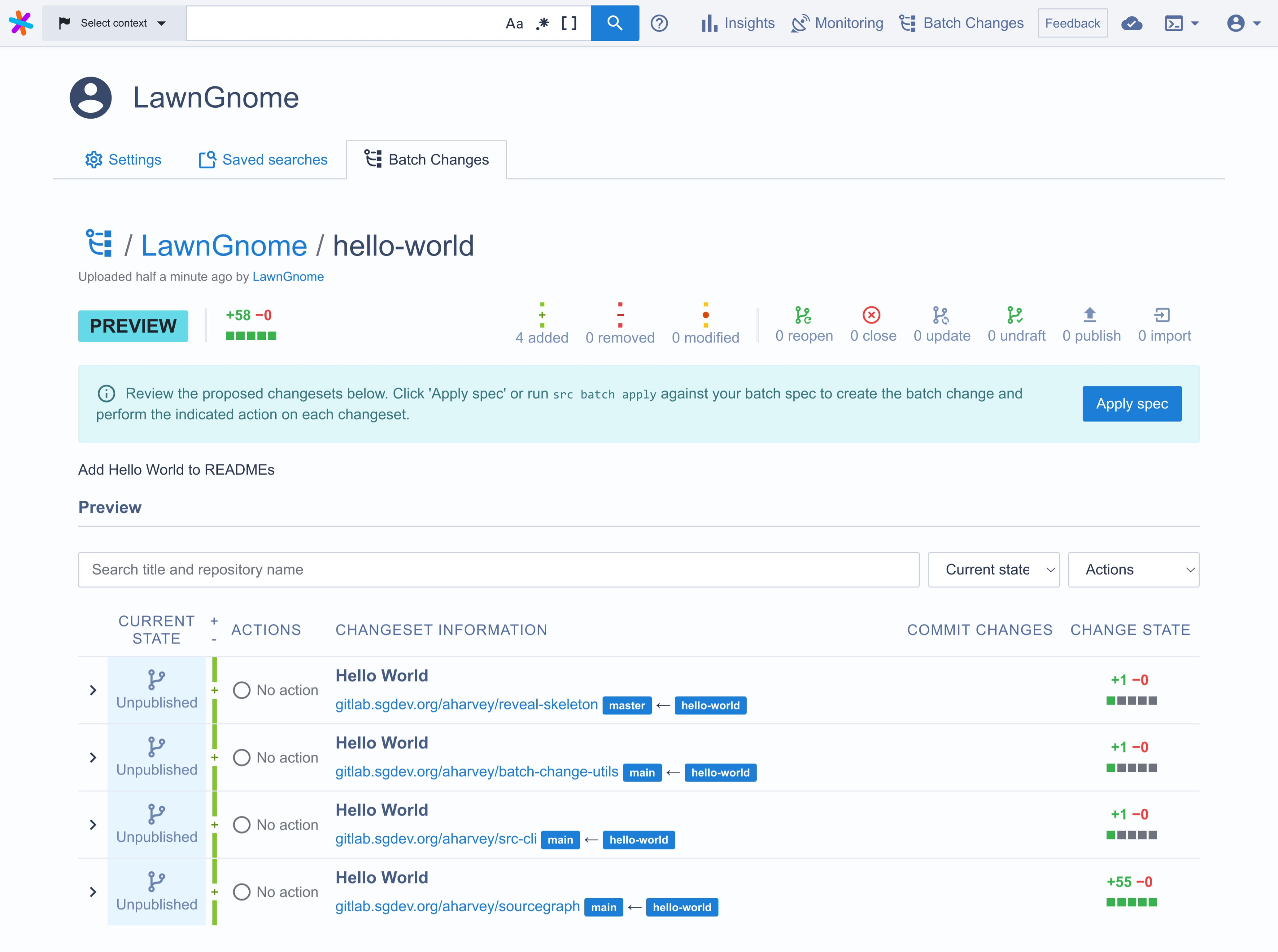
-
Click the Apply button to create the batch change.
After you've applied a batch spec, you can publish changesets to the code host when you're ready. This will turn the patches into commits, branches, and changesets (such as GitHub pull requests) for others to review and merge.
You can share the link to your batch change with other people if you want their help. Any person on your Sourcegraph instance can view it in the batch changes list.
If a person viewing the batch change lacks read access to a repository in the batch change, they can only see limited information about the changes to that repository (and not the repository name, file paths, or diff).
You can update a batch change's changes at any time, even after you've published changesets. For more information, see Updating a batch change.
Applying a batch spec without preview
You can use Sourcegraph CLI (src) to directly apply a batch spec to create or update a batch change without having to use the UI.
Instead of running src batch preview you run the following:
src batch apply -f YOUR_BATCH_SPEC.batch.yamlThis command won't print a link to a preview. It will create or update the batch change it describes directly.
That can be useful if you just want to update a single field in the batch spec, i.e. the description or the changesetTemplate.body, or if you want to continously update a batch change by running src in a CI workflow.
Creating a batch change in a different namespace
Batch changes are uniquely identified by their name and namespace. The namespace can be any Sourcegraph username or the name of a Sourcegraph organization.
By default, batch changes will use your username on Sourcegraph as your namespace. To create batch changes in a different namespace use the -namespace flag when previewing or applying a batch spec:
src batch preview -f your_batch_spec.batch.yaml -namespace USERNAME_OR_ORGWhen creating a batch change server-side using the UI, you can select the namespace for the batch change to belong to at the time that you're creating it.
Administration
Once a batch change is open, any Sourcegraph user can view it. However, the namespace determines who has the ability to administer it, such as editing or deleting it. When a batch change is created in a user namespace, only that user (and site admins) can administer it. When a batch change is created in an organization namespace, all members of that organization (and site admins) can administer it.